
Consequently, the test sources of B are also included in the corresponding classpaths. If your module (say, module A) depends on another module (module B), IntelliJ IDEA assumes that the test sources in A depend not only on the sources in B but also on its own test sources. IntelliJ IDEA processes dependencies for test sources differently from other build tools (for example, Gradle and Maven). The Export option lets you control the compilation classpath for the modules that depend on this one: the marked items will be included in the compilation classpath of the dependent module. Provided: used for building and testing a project. Runtime: included in the classpath for your sources and test sources but only at the run phase. Test: required to compile and run unit tests. Select the necessary scope from the list in the Scope column:Ĭompile: required to build, test, and run a project (the default scope). The classpath may be different when your sources are compiled, your test sources are compiled, your compiled sources are run, your tests are run. Specifying a dependency scope allows you to control at which step of the build the dependency should be used. Configure a dependency scope Specify a dependency scope If IntelliJ IDEA finds no dependency usages in the project, you will be prompted to remove this dependency. After you analyze all necessary dependencies, you can close the Project Structure dialog and view the results. The result of each analysis will be opened in a separate tab of the Dependency Viewer tool window. You can analyze several dependencies one by one without closing the dialog. Right-click the necessary dependency and select Analyze This Dependency. If you want to check whether a dependency still exists in your project, and find its exact usages, you can run dependency analysis: Select the dependency that you want to remove and click or press Alt+Delete. You can also use the Find Usages option of the context menu. To do so, select the necessary dependency and press Alt+F7. Module Dependency: select another module in the project.īefore removing a dependency, make sure that it is not used in other modules in the project. Library: select an existing library or create a new one and then add it to the list of dependencies. JARs or directories: select a Java archive or a directory from files on your computer. Add a new dependencyįrom the main menu, select File | Project Structure Ctrl+Alt+Shift+S and click Modules | Dependencies.Ĭlick Alt+Insert and select a dependency type: If you're using a build tool, such as Maven or Gradle, make all changes using the build file.

This information is valid for projects that are built with the native IntelliJ IDEA builder.
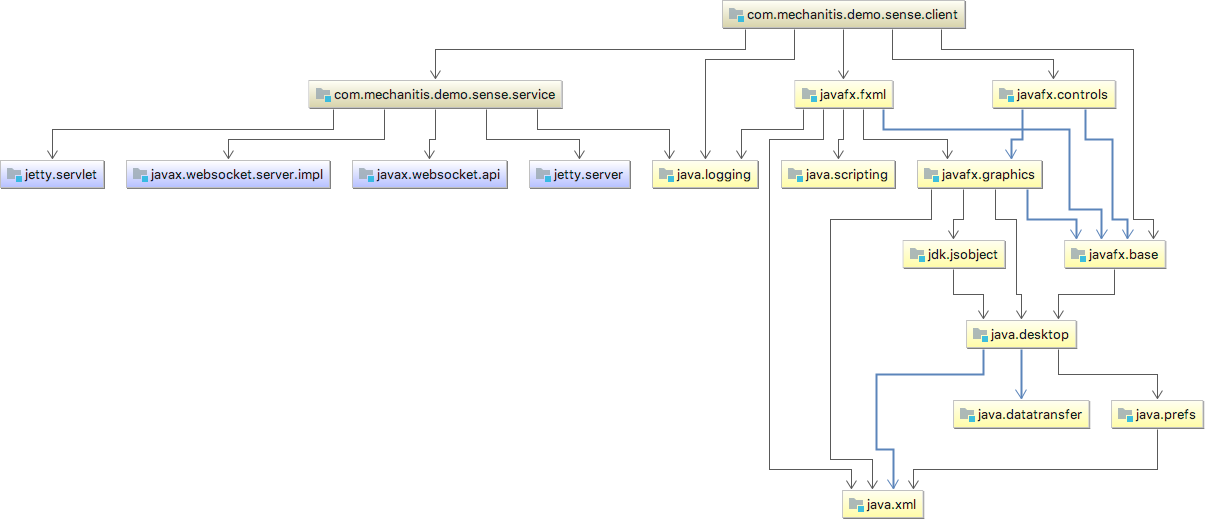
When you compile or run your code, the list of module dependencies is used to form the classpath for the compiler or the JVM. Modules can depend on SDKs, JAR files (libraries) or other modules within a project.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
